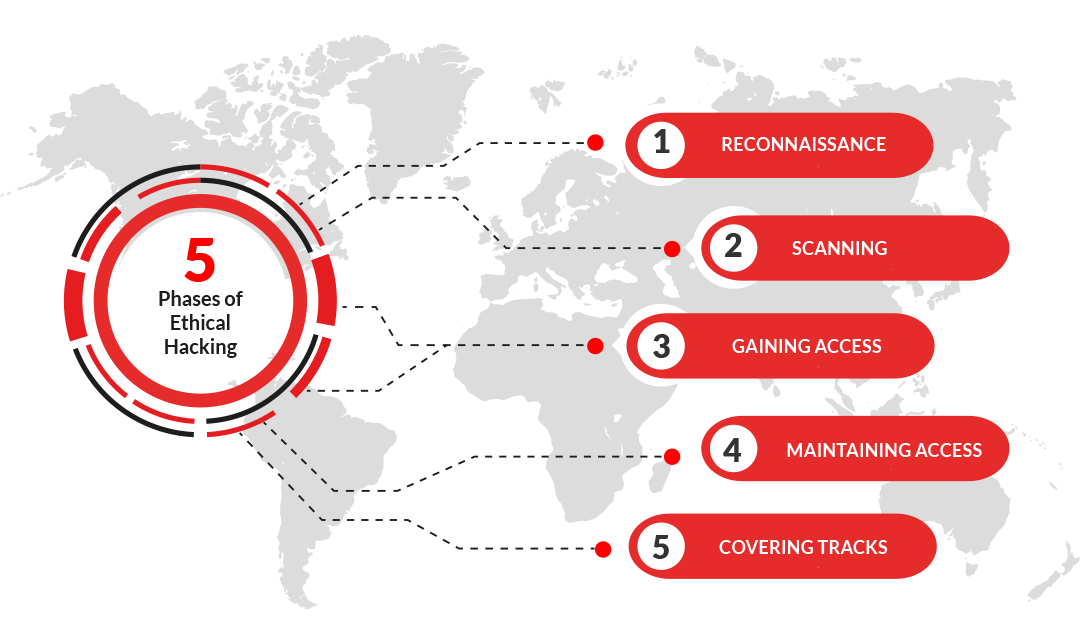
5 Stages of Ethical Hacking
Information Gathering / Reconnaissance
It could be Active or Passive. An example of Passive reconnaissance is when we are given a client and then we go on google to search about that client.
On the otherhand, Active reconnaissance is when we use tools such as Nmap, Nikto or Nessus to scan actively against a client to look for open ports and vulnerabilities.
Note: Active reconnaisance kind of falls into the second stage, which is Scanning and Enumeration.
Passive Reconnaissance
It has two types, Physical and Social. Physical means actually going on site and doing a physical engagement while Social, is for example, doing a phishing assessment.
Location Information: Satellite images, Drone recon, Building layout (badge readers, break areas, security, fencing)
Job Information: Employees (name, job title, phone number, manager, etc.), Pictures (badge photos, desk photos, computer photos, etc.)
Web / Host Assessment
The first thing we really need to do, is what is called Target Validation because there might be situations where a client gives us the wrong IP address and we are off attacking somebody else’s website.
Furthermore, we should look for Subdomains, then carry out Fingerprinting (knowing what’s running on a website or what’s running on a host or knowing the type and version of web server its running). Lastly, we should look into Data breaches because it is the most common way of doing an external assessment that we get into networks. Data breaches are breached incidents from the past that have leaked data.
- Target validation tools: WHOIS, nslookup, dnsrecon
- Finding Subdomains tools: Google Fu, dig, Nmap, Sublist3r, Bluto, crt.sh
- Fingerprinting tools: Nmap, Wappalyzer, WhatWeb, BuiltWith, Netcat
- Data Breaches tools: HaveIBeenPwned, BreachParse, WeLeakInfo
Note: If we go out to a website, it is on the border of Active but as long as we are not scanning it, it is still Passive reconnaissance. Also, some of these tools might change or be deprecated in the future but the methodology don’t.
Discovering Email Addresses
There are tools and websites to discover and verify clients’ email addresses. Some are:
- Hunter.io
- Clearbit : it has to be used with google chrome. To download the chrome extension for clearbit, search for Clearbit Connect on google.
- Emailhippo : can be used to verify email addresses.
- Email-Checker
Note: Do not underestimate Forgot password. It can be use to also verify emails. After entering the target’s email, click enter and click on forgot password. From there we can verify if the email is authentic.
Gathering information from breached credentials
When gathering information from breached credentials, we should look out for potential repeat offenders (users that use the same username more than once as their credential).
Credential stuffing is when we collect account credentials (typically usernames or email addresses and the corresponding passwords) from data breach, and then use these credentials to gain access to user accounts on other systems. We can also make modifications to the passwords like changing some characters to upper or lower cases.
Hunting Breached Credentials
Dehashed is a website for getting breached credentials. We have the ability to search by email, username, ip, etc.
If we are hunting down an individual and we are trying to tie them to other accounts, Dehashed is incredibly useful if we can find their data in a breach database and find a password that is unique. Then we can search for that password and maybe find them somewhere else.
Hunting Subdomains
It is about web information gathering.
- The first and most important thing to do when it comes to websites or bug hunting is that we need to identify what subdomains are out there. Sublist3r is a tool use to identify subdomains.
To install sublist3r in your terminal
1
apt install sublist3r
Note: don’t forget to switch to root user to run the command, use sudo su to change to root user.
After installing it, enter sublist3r in terminal to confirm. Then use
sublist3r -d <domain-name>to search for subdomains and usesublist3r -horsublist3r --hto access the help manual. Ex: sublist3r -d tesla.comcrt.sh is another website to search for subdomains. Use
%before the website name you want to search for, before hitting enter. Ex: %tesla.comowasp amass is another useful tool for in-depth attack surface mapping and asset discovery.
httprobe is a tool to check for working HTTP and HTTPS servers.
Note: Subdomain hunting is very important because it prevents us from limiting our scope to just the main website.
Identifying Website Technologies
Being able to identiy technologies used on a website or service helps us gather imperative information that we could use for enumeration and find exploits and/or vulnerabilities. For example, some of the tools below can help us identify not just the technology used but also the version.
builtwith is a website to identify the frameworks used to build a domain or website.
Wappalyzer is also another great tool to identify website technologies and it has a web browser extension that is easy to utilize. Note: Wappalyzer is considered active reconnaissance.
whatweb is an built-in tool in kali linux terminal that can be used also.
Information Gathering with Burp Suite
Burp Suite is a Web proxy, which means that it has the capability of intercepting traffic.
Setting up Burp Suite
Open up Burp suite and a web browser (i.e firefox). Then click on the hamburger on the top right of your web browser to access the settings page
Scroll all the way down in the settings page and select settings under
Network ProxyThen select
Manual proxy configurationand use 127.0.0.1 and 8080 for the port inHTTP Proxy. Lastly, check Use this proxy server for all protocols checkbox and hit OK at the bottomLeave the settings page tab open and open another tab
In the new tab, go to https://burp or http://burp
This should take you to Burp Suite Community Edition page and you should see
CA Certificateon the top rightClick on
CA Certificateto download itHead back to the settings page tab and go to
Privacy & Security>View Certificates>import>Downloads>cacert.der>openCheck the two checkboxes that shows up after the hitting open
Using Burp Suite
While Burp Suite app is running, search for the website you want on your web browser (i.e firefox)
In Burp Suite app, the
Proxytab should be lit up in orange color. This means that it is intercepting requests that the website is making outYou can click
Forwardto capture all different types of traffic. Note: intercepter should be turned onYou can also go to the
Targettab to see all the traffic that has been intercepted so far
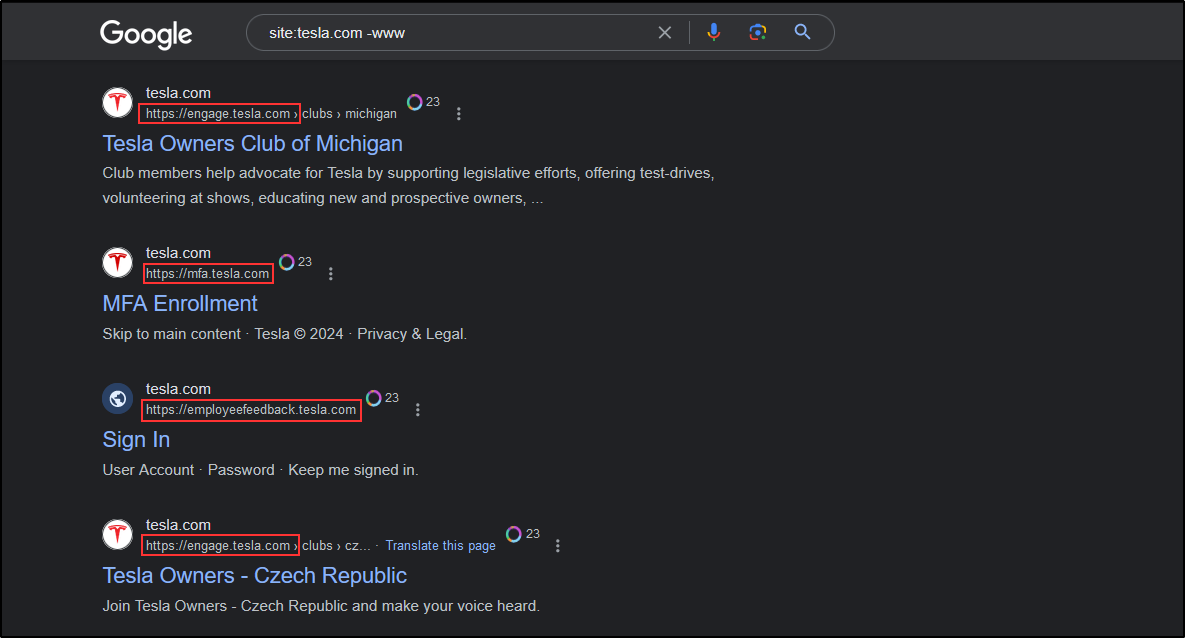
Google Fu
Utilizing google search operators can help optimize and narrow down our search in finding subdomains as well as in gathering information on the web.
For example, we can use the site operator with -www flag to search for subdomains on google.
Utilizing Social Media
We can use platforms like Linkedin or Twitter to find useful information about our target by checking the photo/images page to look for employee badges in the pictures posted or checking the people page on Linkedin to find targets such as IT or C-Suite personnel. And a good way to find badges is to utilize social media.
Note: Use a sock puppet account when trying to gather information a target.
Scanning & Enumeration
Is when we use tools such as Nmap, Nikto or Nessus to scan actively against a client to look for open ports and vulnerabilities.
Enumeration means looking at items and digging into them to see if anything of value can be found. Ex: we found a web server running on port 80, open and its running on something like Apache 1.2, and then we research on google if there are any exploits on Apache 1.2.
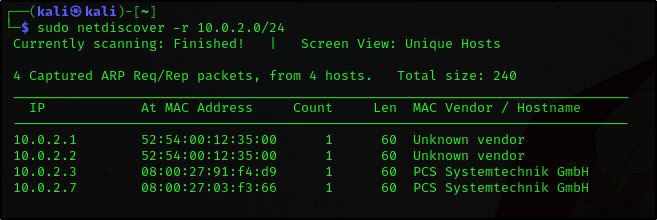
We can use an active/passive ARP reconnaissance tool called netdiscover to detect all hosts/machines on a given network.
1
netdiscover -r <ip-address/subnet>
Exploitation / Gaining Access
Is when we run an exploit against a client or vulnerable service to gain access to a machine, network, or an environment. Once we have that access, the process starts to repeat and we perform scanning & enumeration again.
Maintaining Access
if we were to get kicked out or a user shuts down their computer, how do we maintain access when the user turns back on the computer and we still have access to it.
Covering Tracks
An example is, deleting any logs that we may leave behind or deleting any kind of malware we uploaded.
Very Important: The process in methodology never changes regardless if we are doing network, web app or a different of assessment. The 5 stages are very important and can be asked in interviews.
Disclaimer
These notes are for ethical and educational purposes only. Please, do not use them for malicious intent.